Pregnancy & Vomiting
Call a healthcare provider if self-care at home does not help reduce the symptoms, or if you are unable to take (and keep down) any liquids for more than 24 hours. Also call when you vomit on and off, but more than usual, or if the vomiting is associated with these symptoms, which may stem from other causes:
Go to a hospital's emergency department when you vomit continually and you have these symptoms of dehydration:
Self-Care at Home
As miserable as it may seem, nausea and vomiting are usually part of a healthy
pregnancy. The misery typically goes away by the middle of the second trimester. You can try home remedies to reduce your symptoms, and if these do not work, your doctor can help.
No single treatment works best for every woman with nausea and vomiting during
pregnancy. Different techniques work for different women. You will have to discover what seems to make your symptoms better. Many women have found the following suggestions helpful:
Diet
- Eat small amounts of food frequently so that you are never too hungry or too full.
- Avoid spicy and fatty foods, and foods with odors that bother you.
- Try eating simple carbohydrates, such as saltine crackers, unbuttered toast, plain baked potatoes, white rice, gelatin desserts, broth, pretzels, popsicles, herbal or decaffeinated tea with sugar, or non-diet ginger ale.
- Combine these simple carbohydrates with a serving of protein, especially right before bed to minimize swings in blood sugar that may contribute to nausea.
- Drink liquids between meals and not during meals to minimize nausea and vomiting.
- Keep crackers at the bedside table to help with nausea in the morning.
Vitamin supplements
If you find that your prenatal vitamin seems to worsen your nausea, take it with food instead of on an empty stomach. If this does not help, talk to your doctor about the possibility of switching to a different vitamin. Chewable vitamins are sometimes easier to tolerate.
Some evidence suggests that pyridoxine (vitamin B-6) supplements help reduce nausea and vomiting. The suggested dose is 25-50 mg every eight hours, and it can be given as an injection up to 200 mg. There are no known harmful effects of vitamin B-6 taken at these doses. Some prenatal vitamins are formulated with extra vitamin B-6.
Acupressure
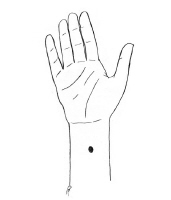
Stimulation of the P6 (Nei Guan)
acupressure point on the wrist (on the inside of the wrist about where a watchband is worn) has been suggested as a method to reduce nausea and vomiting.
You can press on this area with your finger or thumb or buy an
acupressure band. These bands are often sold as motion sickness treatments, so check with a local drug store or auto club.
Hypnosis
- Medical hypnosis has been used to reduce nausea and vomiting.
- Some women have also used self-hypnosis to control their symptoms.
- If you want to try hypnosis, make sure you work with an experienced professional.
Over-the-counter medications
Solutions containing glucose, fructose, and phosphoric acid are available over-the-counter. These solutions may reduce muscle contractions in the wall of the stomach and intestines. The normal dose is 1-2 tablespoons every 15 minutes for no more than 5 doses. These solutions cause no known harmful effects on the fetus.
Two over-the-counter antihistamines, diphenhydramine (Benadryl) and dimenhydrinate (Dramamine), have been shown to improve nausea and vomiting. Although both are generally believed to be safe in
pregnancy, you should discuss the risks and benefits of these
medications with your doctor.
Herbal remedies
- Powdered ginger is used fairly commonly in Europe as a nausea remedy during pregnancy.
- The usual dose is 250 mg, three times daily.
- The effect of ginger on the fetus has not been extensively studied.
Follow-up
- Follow the home care suggestions that seem to help your symptoms.
- If your doctor prescribes any medications, take them as directed.
Prevention
You may not be able to prevent nausea during the early part of your pregnancy, but you can minimize your symptoms. It can become a vicious cycle, where nausea leads to vomiting, which leads to dehydration , which leads to more nausea. The earlier you can control the symptoms, the better.
"Take home" suggestions to remember:
- Nausea and vomiting during pregnancy usually last several weeks.
- No one thing helps everyone.
- Get to know what techniques work best for you and use them.
Outlook
Most women who experience nausea and vomiting during the early part of pregnancy go on to have healthy babies. In fact, some evidence indicates that women with mild-to-moderate nausea and vomiting are less likely to miscarry than are women who experience no symptoms at all. Some experts say that mild nausea and vomiting in pregnancy might have served some evolutionary advantage for early humans.
- Women with very severe symptoms, especially with
dehydration and weight loss , are at higher risk for slowed fetal growth and low birth weight babies.
- Most women improve with IV fluids that may be given for several days without other measures.
- Women with continual vomiting and
dehydration require IV fluid replacement in a medical setting off and on.
- Few women with hyper emesis gravid arum require a prolonged stay in the hospital, usually 7-10 days with continued treatment on an outpatient basis for 10-21 days.
- While in the hospital or as an outpatient, you may require a nasal feeding tube for placing fluid into your stomach or an IV to place fluid into a blood vessel.